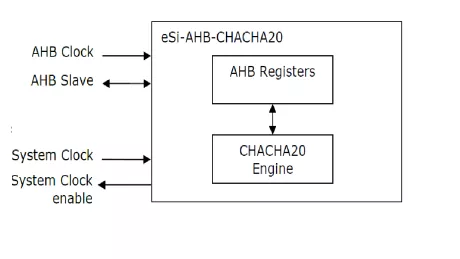
TLS accelerator IP
Filter
Compare
12
IP
from
8
vendors
(1
-
10)
-
PKC Multi Hardware Accelerator IP
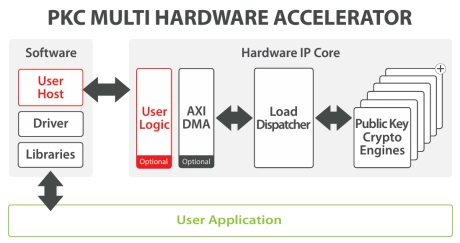
- The PKC Multi hardware accelerator is a secure connection engine that can be used to offload the compute intensive Public Key operations (Diffie-Hellman Key Exchange, Signature Generation and Verification), widely used for High-performance TLS Handshake.
-
High-Speed Elliptic Curve Cryptography Accelerator for ECDH and ECDSA
- Fully digital design
- Portable to any ASIC or FPGA technology
- Fully standard compliant
- Easy to integrate
-
Single instance HW Lattice PQC ultra accelerator
- PQPerform-Flare is a powerful hardware-based FIPS 140-3 CAVP-certified product, designed for high throughput and low latency PQC.
- It adds PQC for applications that typically handle a large number of transactions, such as high-capacity network hardware applications and secure key management HSMs.
-
HMAC-SHA256 cryptographic accelerator
- Hardware Root of Trust
- Widely used password hash algorithm
- Security Critical HTTP, SSL, TLS
- Key storage in Private memory

-
HMAC-SHA256 Secure Core - Hardware Accelerator for SHA-2 and HMAC with Low Latency SCA/FI Protection
-
Hardware Accelerator for SHA-2 and HMAC with Low Latency SCA/FI Protection
-
-
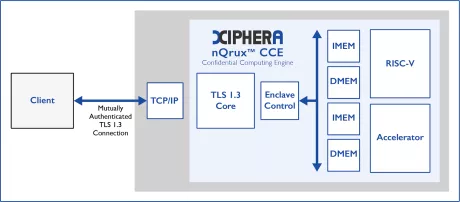
nQrux™ Confidential Computing Engine (CCE)
- Complete physical isolation of code & data
- Secure code & data transmission with TLS 1.3 Quantum-safe crypto option
-
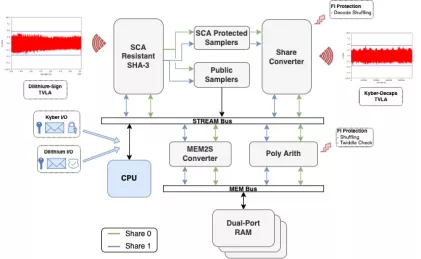
Unified Hardware IP for Post-Quantum Cryptography based on Kyber and Dilithium
- Turn-key implementations of the NIST FIPS recommended CRYSTALS post-quantum for key encapsulation (KEM) and digital signature algorithm (DSA)
-
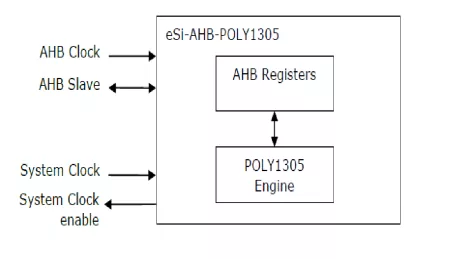
Poly1305 core
- Processing of a 128-bit dataword in as low as 4 clock cycles
- Different processing architectures offering different balances between throughput/area
- Fixed time processing for resistance against timing attacks
- Simple register-based interface
-
Combined ChaCha20 and Poly1305 core
- Multiple processing modes:
- Chacha20 processing of 64-bytes in as low as 13 clock cycles
- Poly1305 processing of 16-bytes in as low as 4 clock cycles
- Different processing architectures offering different balances between throughput/area
-
ChaCha20 stream cipher core
- Simple register based interface
- Processing of 64-bytes in as low as 13 clock cycles
- Selection between High Throughput or Low Gate-Count architectures
- Real-time selection between key generation or cipher/decipher modes