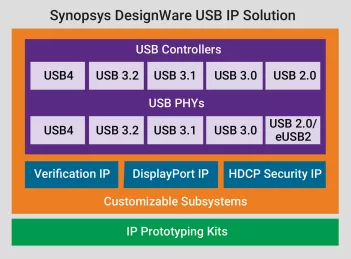
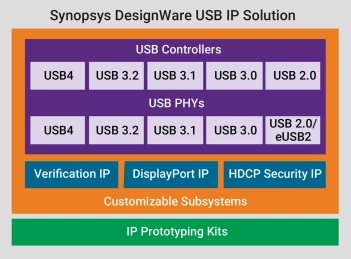
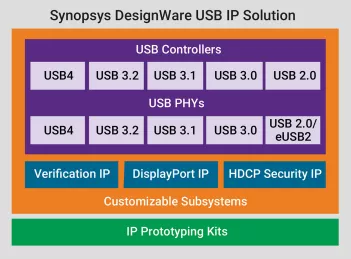
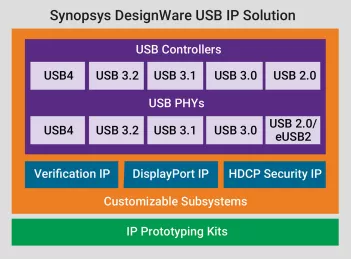
USB 4.0 IP
Filter
Compare
191
IP
from
25
vendors
(1
-
10)
-
USB 4.0 V2 PHY - 4TX/2RX, TSMC N3P , North/South Poly Orientation
- Supports 40 Gbps, 20 Gbps, 10 Gbps, and 5 Gbps data rates
- Supports 480 Mbps, 12 Mbps, and 1.5 Mbps data rates
- x1 and x2 configurations (USB 3.2 and USB 3.1 PHY only)
- Low active and standby power
- Small area for low silicon cost
-
USB 4.0 - Enables fast data transfer, efficient power delivery, and connectivity
- USB 4.0 is the third major revision of the USB standard, offering data transfer speeds up to 20 Gbps via dual-lane operation. It supports multiple transfer modes and improved bandwidth utilization for high-speed applications.
- USB 4.0 enables seamless connectivity across various devices, from storage and printers to high-performance audio and video equipment. It enhances power delivery and ensures efficient data transfer for consumer electronics, networking, and industrial applications.
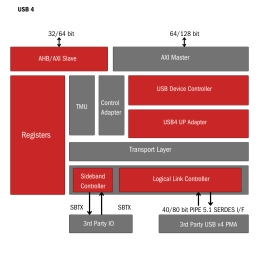
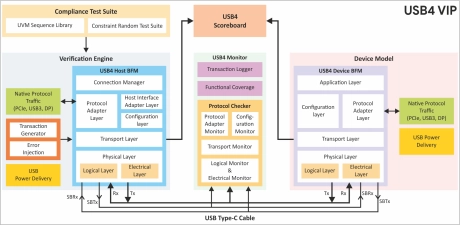
-
USB 4.0 Verification IP
- Fully compliant with USB4 specification v1.0 (March 2022) and Connection Manager version 1.0.
- Supports USB3.2 Specification, Revision 1.1 and backward compatibility to USB2.0.
- Supports USB Power Delivery Release 3.1, Version 1.8 and Type-C v2.2.
- Supports Thunderbolt (TBT3) interoperability.
-
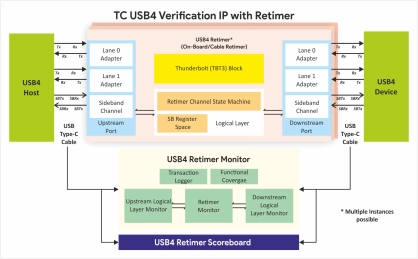
USB 4.0 Retimer Verification IP
- Fully compliant with USB4 specification v1.0 (March 2022), Connection Manager version 1.0 and USB4 Re-Timer Specification Rev 1.0.
- Supports USB3.2 Specification, Revision 1.1 and backward compatibility to USB2.0.
- Supports USB Power Delivery Release 3.1, Version 1.8 and Type-C v2.2.
- Supports Thunderbolt (TBT3) interoperability.
-
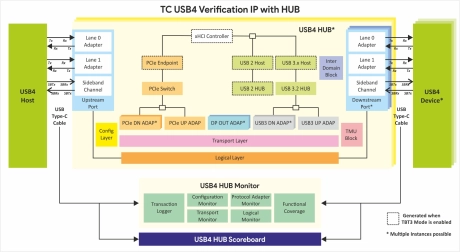
USB 4.0 HUB Verification IP
- Fully compliant with USB4 specification v1.0 (March 2022) and Connection Manager version 1.0
- Supports USB3.2 Specification, Revision 1.1 and backward compatibility to USB2.0.
- Supports USB Power Delivery Release 3.1, Version 1.8 and Type-C v2.2.
- Supports Thunderbolt (TBT3) interoperability.
-
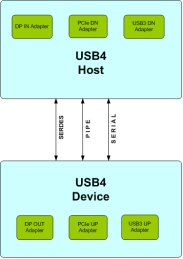
USB 4.0 Verification IP
- Compliant with USB4.0 Specification
- Supports USB4.0 Gen2 and Gen3 Operation
- Supports constrained randomization of protocol attributes
- Supports all types of error injection and detection
-
USB 2.0 picoPHY - UMC 40LP25, OTG
- Ported to over 50 different processes and configurations ranging from 65-nm to 14/16-nm FinFET
- Supports the USB 2.0 protocol and data rate (480 Mbps)
- Supports the USB Type-C specification
- USB femtoPHY, USB nanoPHY and USB picoPHY offer a tunability feature that allows quick, post-silicon adjustments that occur due to process variations, or unexpected chip and board parasitic, without modifying the existing design
-
USB 2.0 femtoPHY - TSMC 40ULPeF25 x1, OTG
- Ported to over 50 different processes and configurations ranging from 65-nm to 14/16-nm FinFET
- Supports the USB 2.0 protocol and data rate (480 Mbps)
- Supports the USB Type-C specification
- USB femtoPHY, USB nanoPHY and USB picoPHY offer a tunability feature that allows quick, post-silicon adjustments that occur due to process variations, or unexpected chip and board parasitic, without modifying the existing design
-
USB 2.0 femtoPHY - TSMC 40ULP25 x1, OTG, Type-C
- Ported to over 50 different processes and configurations ranging from 65-nm to 14/16-nm FinFET
- Supports the USB 2.0 protocol and data rate (480 Mbps)
- Supports the USB Type-C specification
- USB femtoPHY, USB nanoPHY and USB picoPHY offer a tunability feature that allows quick, post-silicon adjustments that occur due to process variations, or unexpected chip and board parasitic, without modifying the existing design
-
USB 2.0 nanoPHY - TSMC 40LP252P
- Ported to over 50 different processes and configurations ranging from 65-nm to 14/16-nm FinFET
- Supports the USB 2.0 protocol and data rate (480 Mbps)
- Supports the USB Type-C specification
- USB femtoPHY, USB nanoPHY and USB picoPHY offer a tunability feature that allows quick, post-silicon adjustments that occur due to process variations, or unexpected chip and board parasitic, without modifying the existing design