Post-Quantum Cryptographic IP
Filter
Compare
29
IP
from
13
vendors
(1
-
10)
-
IoT device security platform with a hybrid post-quantum cryptographic algorithm
- Software development lifecycle integration (SDLC, CI/CD)
- Key and certificate management (PKI/CLM)
- On-device security features (e.g. secure boot, flash encryption)
- On-device key generation & storage

-
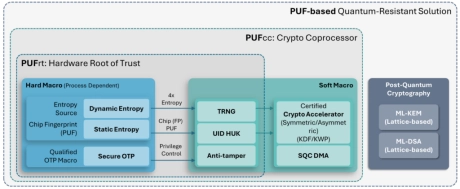
PUF-based Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC) Solution
- PUFsecurity is proud to pioneer the world’s first PUF-based Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC) solution, delivering cutting-edge, hardware-level security that sets a new standard.
- Our innovative solution integrates PUF technology with quantum-resistant cryptographic algorithms, ensuring robust key protection and seamless transition to a quantum-secure future.
-
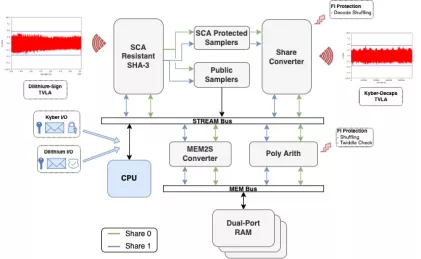
High-Performance Hybrid Classical and Post-Quantum Cryptography
- The High-Performance Hybrid Cryptography IP core delivers accelerated support for both classical (RSA, ECC) and post-quantum (ML-KEM, ML-DSA) algorithms in a unified architecture optimized for maximum throughput.
-
Hybrid Classical and Post-Quantum Cryptography
- The Hybrid Cryptography IP core combines traditional asymmetric algorithms—such as RSA and ECC—with post-quantum standards including ML-KEM (Kyber) and ML-DSA (Dilithium)—in a single, efficient hardware module.
-
Post-Quantum Digital Signature IP Core
- The KiviPQC-DSA is an IP core implementing the ML-DSA (Module-Lattice-based Digital Signature Algorithm) a post-quantum cryptographic standard defined by NIST FIPS 204.
- Designed to withstand both classical and quantum computer attacks, ML-DSA ensures the authenticity and integrity of signed data far into the future.
-
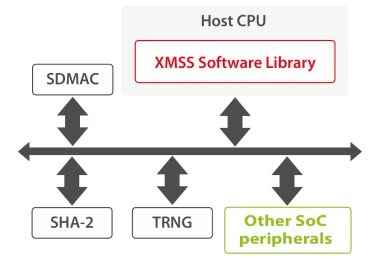
XMSS Post-Quantum Cryptography IP
- XMSS is a Post-Quantum Cryptographic (PQC) algorithm, meaning it is mathematically designed to be robust against a cryptanalytic attack using a quantum computer.
- XMSS is a stateful Hash-Based Signature Scheme that has been recommended by NIST in 2020.
-
Cryptographic Cores IP
- The Cryptographic Cores IP portfolio delivers secure, high-performance implementations of symmetric, asymmetric, and post-quantum algorithms.
- Designed for low-area, low-latency operation, the silicon-proven cores help SoC designers and embedded teams build trusted, efficient devices for IoT, automotive, medical, and industrial markets.
-
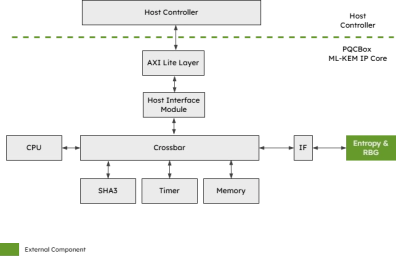
Post-Quantum Key Encapsulation IP Core
- The PQC-KEM is an IP Core for ML-KEM Key Encapsulation that supports key generation, encapsulation, and decapsulation operations for all ML-KEM variants standardized by NIST in FIPS 203.
- ML-KEM is a post-quantum cryptographic (PQC) algorithm, designed to be robust against a quantum computer attack.
-
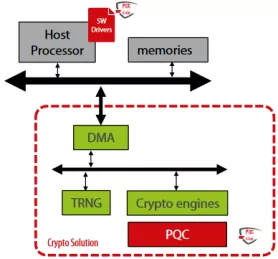
Crypto Coprocessor with integrated Post-Quantum Cryptography IPs
- The Crypto Coprocessors are a hardware IP core platform that accelerates cryptographic operations in System-on-Chip (SoC) environment on FPGA or ASIC.
- Symmetric operations are offloaded very efficiently as it has a built-in scatter/gather DMA. The coprocessors can be used to accelerate/offload IPsec, VPN, TLS/SSL, disk encryption, or any custom application requiring cryptography algorithms.
-
Unified Hardware IP for Post-Quantum Cryptography based on Kyber and Dilithium
- Turn-key implementations of the NIST FIPS recommended CRYSTALS post-quantum for key encapsulation (KEM) and digital signature algorithm (DSA)