Cortex-M3 IP
Filter
Compare
10
IP
from
5
vendors
(1
-
10)
-
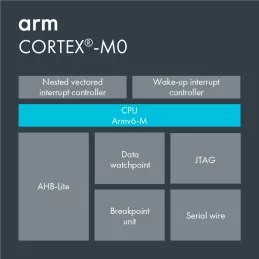
32-bit RISC Processor To Deliver High Performance In Low-Cost Microcontroller Applications
- Powerful debug and non-intrusive real-time trace - Comprehensive debug and trace features dramatically improve developer productivity. It is extremely efficient to develop embedded software with proper debug.
- Memory Protection Unit (MPU) - Software reliability improves when each module is allowed access only to specific areas of memory required for it to operate. This protection prevents unexpected access that may overwrite critical data.
- Integrated nested vectored interrupt controller (NVIC) - There is no need for a standalone external interrupt controller. Interrupt handling is taken care of by the NVIC removing the complexity of managing interrupts manually via the processor.
- Thumb-2 code density - On average, the mix between 16bit and 32bit instructions yields a better code density when compared to 8bit and 16bit architectures. This has significant advantages in terms of reduced memory requirements and maximizing the usage of precious on-chip Flash memory.
-
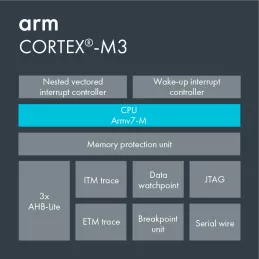
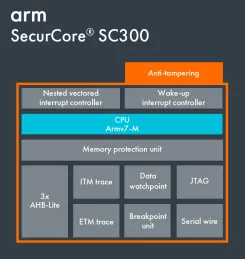
Tamper-resistant Cortex-M processor with optional software isolation using TrustZone for Armv8-M
- Tamper-resistant Cortex-M processor with optional software isolation using TrustZone for Armv8-M
-
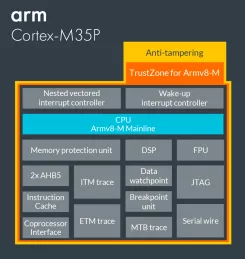
Arm Cortex-M33
- TrustZone for Armv8-M - A foundation for security for embedded devices. TrustZone offers software isolation to code, memory and I/O while retaining the requirements of embedded applications: real-time deterministic response, minimal switching overhead, and ease of software development.
- Co-processor interface - A dedicated bus for extending the operation of the processor with tightly coupled co-processors to handle frequent and compute intensive operations in an ecosystem friendly manner. The interface supports up to eight accelerators and takes into account the security state of the co-processor.
- SIMD, saturating arithmetic, fast MAC - Powerful instruction set for accelerating DSP applications, built right into the processor. A highly optimized DSP library built using these instructions is available free-of-charge from the Arm website (CMSIS Library).
- Memory Protection Unit (MPU) - Software reliability and system security improves when each module is allowed access only to specific areas of memory required for it to operate. This protection prevents unexpected access that may overwrite critical data. Each of the security zones can have a dedicated MPU that may be configured with a different number of regions.
-
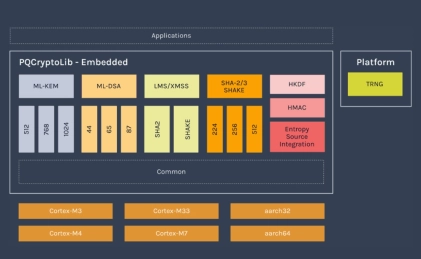
Highly-optimized PQC implementations, capable of running PQC in under 15kb RAM
- PQCryptoLib-Emebedded is a versatile, CAVP-ready cryptography library designed and optimized for embedded devices.
- With its design focused on ultra-small memory footprint, PQCryptoLib-Embedded solutions have been specically designed for embedded systems, microcontrollers and memory-constrained devices. It provides a PQC integration to devices already in the field.
-
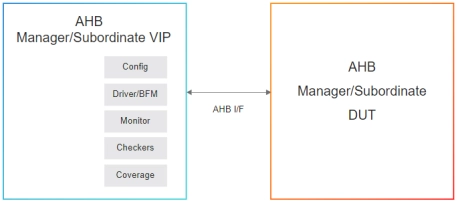
Simulation VIP for AMBA AHB
- Multiple Agents
- Can support any number of agents
- Data and Address Widths
- Supports all legal data and address widths
-
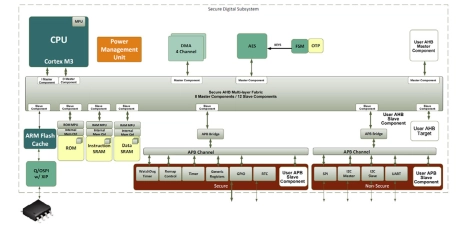
AHB Secure Subsystem - ARM Cortex M3
- The Secure AHB Performance Subsystem is a high-performance AHB subsystem that allows for a high level of hardware and software security.
- It integrates a security-conscious processor, the ARM Cortex-M3, with a security-conscious low power high-performance subsystem.
- Everything is pre-integrated with the necessary AHB and APB IP cores needed to run a small software kernel or a Real Time Operating System (RTOS).
-
Telematics Processors IP
- Core and infrastructure
- ? ARM® Cortex™-R4 MCU
- ? Embedded SRAM
- ? SDRAM controller
-
-
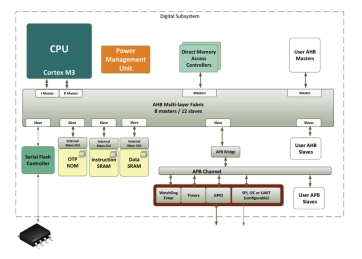
AHB Performance Subsystem - ARM Cortex M3
- The AHB Performance Subsystem is an AMBA® based system that is useful as the digital infrastructure for building low power SOCs needing additional performance.
- This AHB Multi-matrix system contains a flexible Power Management Unit for controlling power sequencing of the CPU and peripherals.
- The PMU can easily be extended to control additional cores, peripherals and even analog subsystems on the same SOC.
-
Small, Low Power, Energy Efficient 32-bit Microcontroller Processor
- Exceptional code density - on average, the mix between 16-bit and 32-bit instructions yields a better code density when compared to 8-bit and 16-bit architectures. This has significant advantages in terms of reduced memory requirements and maximizing the usage of precious on-chip Flash memory.
- Binary upward compatible with all other Cortex-M processors - the Cortex-M0 has mainly 16-bit Thumb-2 instructions and few 32-bit ones. These instructions are also present on all the other Cortex-M processors. Hence all code written for the Cortex-M0 will run as is on the other processors.
- Built-in low-power features - sleep, deep sleep and state retention are three low power modes available to the user
- Optional Debug Access Port and Serial Wire Debug - for devices where every pin counts the serial wire debug port uses only two pins