CAST IP
Filter
Compare
133
IP
from
2
vendors
(1
-
10)
-
Tiny, Ultra-Low-Power Embedded RISC-V Processor
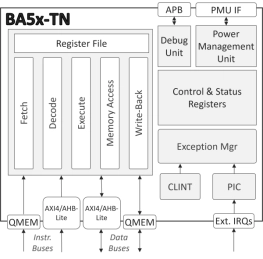
- The BA5x-TN is a compact, ultra-low power, 32-bit, deeply embedded processor IP core.
- With a two-stage execution pipeline, the processor implements the Embedded variant of the base RV32 ISA (RV32E).
- It uses just 16 general-purpose compressed instructions and omits other resource-demanding extensions.
-
Low-Power Embedded RISC-V Processor
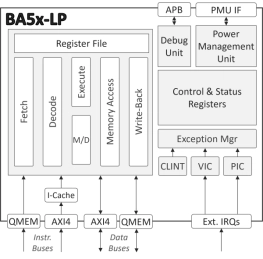
- The BA5x-LP is a highly efficient, low-power, 32-bit, deeply embedded processor IP core.
- The two-stage pipeline processor implements either the RV32I or RV32E instruction set.
- It comes pre-configured with the Multiply/Divide (M) and Compressed Instruction (C) extensions, providing a more flexible and capable platform without a significant increase in area or power.
-
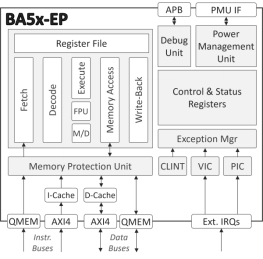
Enhanced-Processing Embedded RISC-V Processor
- The BA5x-EP is a highly-featured 32-bit RISC-V embedded processor IP core optimized for complex, processing-demanding applications.
- It is equipped with a floating-point unit and cache memories, supports hardware-level virtualization, and is suitable for concurrent execution in a multi-processor environment.
-
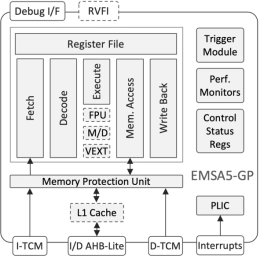
Vector-Capable Embedded RISC-V Processor
- The EMSA5-GP is a highly-featured 32-bit RISC-V embedded processor IP core optimized for processing-demanding applications.
- It is equipped with floating-point and vector-processing units, cache memories, and is suitable for concurrent execution in a multi-processor environment.
-
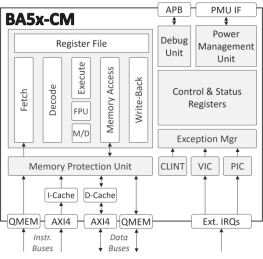
Compact Embedded RISC-V Processor
- The BA5x-CM is a feature-rich 32-bit deeply embedded processor.
- Equipped with a floating-point unit and an instruction cache memory and supporting concurrent execution in a multiprocessor environment, it is well-suited to a wide range of edge IoT and similar applications.
-
Audio Sample Rate Converter
- The ASRC core is a compact and high-performance audio sample rate converter.
- It accurately converts digital audio signals between different sample rates while maintaining signal integrity and minimizing distortion.
- Supporting both asynchronous and synchronous conversion modes, the low latency ASRC can be used in real-time streaming applications as well as in high-speed batch processing environments.

-
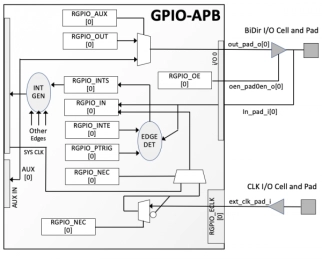
General-Purpose I/O Controller with APB Interface
- User selectable number of GPIO signals from 1 to 32
- All GPIO signals can be bi-directional (external bi-directional I/O cells are required in that case)
- All GPIO signals can be tri-stated or open-drain enabled (external tri-state or open-drain I/O cells are required in that case)
- GPIO signals programmed as inputs can cause an interrupt request to the CPU
-
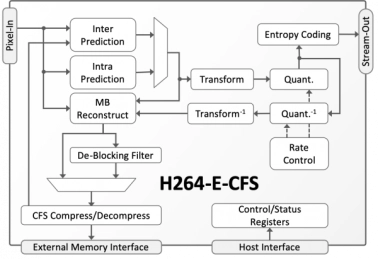
AVC/H.264 Video Encoder with Compressed Frame Store
- Low power AVC/H.264 encoder
- Small silicon footprint
- Optimized for low-latency
- Low-bit-rate video streaming
-
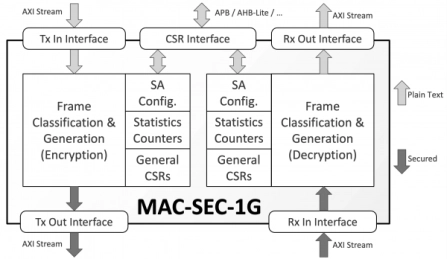
MACsec Protocol Engine for 10/100/1000 Ethernet
- The MAC-SEC-1G IP core implements a compact and configurable custom-hardware protocol engine for the IEEE 802.1AE (MACsec) standard.
- It supports all cipher suites provisioned by the MACsec standard and the VLAN-in-Clear improvement and is silicon- and performance-optimized for networks operating up to 1Gbps.
-
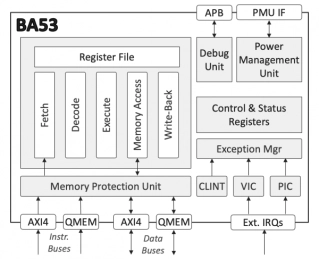
Low-Power Deeply Embedded RISC-V Processor
- The BA53 is a configurable, low-power, deeply-embedded RISC-V processor IP core.
- It implements a single-issue, in-order, 5-stage execution pipeline, and supports the RISC-V 32-bit base integer instruction set (RV32I), or the 32-bit base embedded instructions set (RV32E).