AXI Bridge IP
Filter
Compare
164
IP
from
30
vendors
(1
-
10)
-
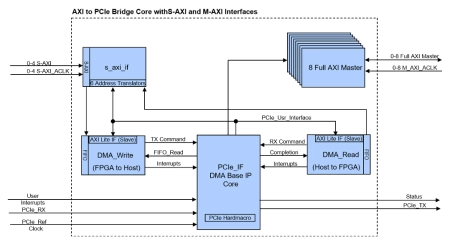
AXI Bridge for PCIe IP Core
- The AXI Bridge for PCIe IP core is the IP solution with a powerful mix of multiple industry standard memory mapped AXI Interfaces.
- The AXI Bridge IP core translates the AXI4 memory read or writes to PCI-Express Transaction Layer Packets and translates PCIe memory read and write requests to AXI4 transactions.
- All interfaces support fully parallel operation without any interferences. Interfaces that are not required can be turned off individually and do not occupy logic resources.
-
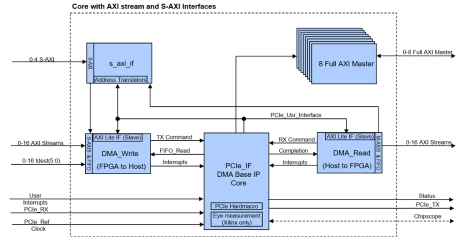
AXI Bridge with DMA for PCIe IP Core
- The AXI Bridge with DMA IP core is the ultimate PCIe DMA IP solution with a powerful mix of multiple industry standard AXI Interfaces.
- AXI Stream interfaces allow continuous data streaming from FPGA to Host or from Host to FPGA. S-AXI Memory mapped interfaces allow easy data access of remote memories in order to realize shared memory access or per to peer applications.
-
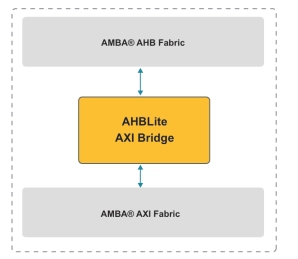
AHB Lite to AXI Bridge
- The AHB Lite to AXI Bridge translates an AHB Lite bus transaction (read or write) to an AXI bus transaction.
- It is expected that the AXI clock and the AHB clock are derived from the same clock source, and that the period of the AHB Lite clock is an integer multiple of the AXI clock in the range [1,16].
-
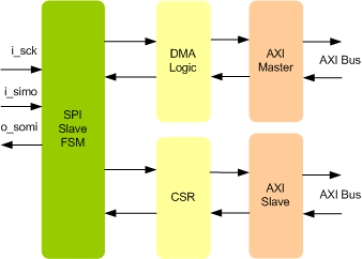
SPI Slave To AXI Bridge IIP
- Compliant with the SPI Block Guide 4.01 standard.
- Full SPI Slave functionality.
- Converts SPI Transactions into AXI write or read instructions
- Allows external devices to access the internal AXI Bus
-
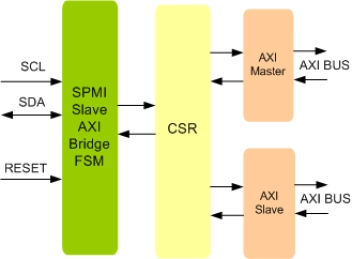
MIPI SPMI Slave AXI Bridge IIP
- Supports 2.0 and 1.0 MIPI SPMI Specification
- Full MIPI SPMI Slave functionality
- Allows external devices to access the internal AXI Bus
- Supports following frames
-
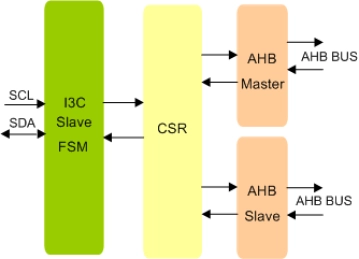
MIPI I3C Slave To AXI Bridge IIP
- Compliant with the I3C version 2.0 specification.
- Full MIPI I3C Slave functionality.
- Convert MIPI I3C Transactions into AXI write or read instructions
- Allows external devices to access the internal AXI Bus
-
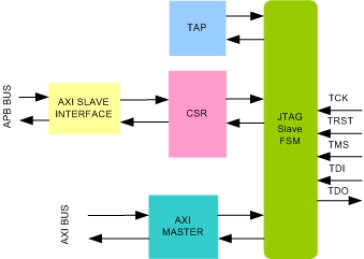
JTAG Slave To AXI Bridge IIP
- Supports Jtag protocol standard IEEE 1149.1 and IEEE 1149.6
- Supports all the JTAG tap instructions.
- Supports programmable clock frequency of operation.
- Supports Instruction register and data register of various sizes.
-
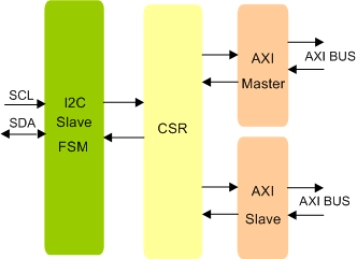
I2C Slave To AXI Bridge IIP
- Compliant with I2C version 6.0 specification
- Full I2C Slave Functionality
- Converts I2C Transactions into AXI write or read instructions
- Allows external devices to access the internal AXI Bus
-
PCI Express to AMBA 4 AXI/3 AXI Bridge
- Complete IP solution consists of digital controllers, PHYs and verification IP
- Fully supports the Synopsys Controller IP for PCI Express Endpoint, Root Port, Dual Mode (EP/RP), and Switch port types
- Fully compliant with the AMBA 3 AXI and 4 AXI interconnects
- Full protocol mapping from PCI Express to the AMBA 3 AXI or 4 AXI bus protocol
-
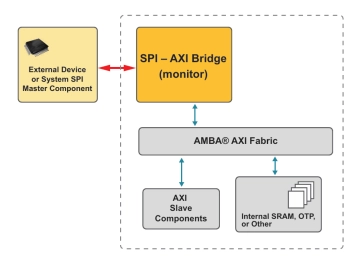
SPI to AXI Bridge
- The SPI to AXI Bridge IP core is commonly used as a monitor interface to allow external devices to access the internal AXI bus.
- A SPI to AXI Bridge provides read/write access by an external SPI device to the various memories and registers that are present in the chip’s internal AXI subsystem via an AXI Master component interface.