ARM Cortex-M0 IP
Filter
Compare
7
IP
from
4
vendors
(1
-
7)
-
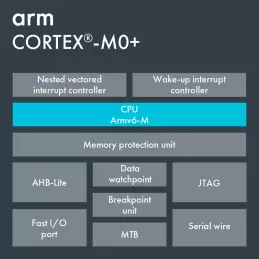
Arm Cortex-M0+
- Memory protection unit - Software reliability improves when each module is allowed access only to specific areas of memory required for it to operate. This protection prevents unexpected access that may overwrite critical data.
- Binary upward compatible with all other Cortex-M processors - The Cortex-M0+ has mainly 16bit Thumb-2 instructions and few 32bit ones. These instructions are also present on all the other Cortex-M processors. Hence all code written for the Cortex-M0+ will run as is on the other processors.
- Built-in low-power features - Sleep, deep sleep and state retention are three low power modes available to the user.
- Optional Debug Access Port and Serial Wire Debug - For devices where every pin counts the serial wire debug port uses only two pins.
-
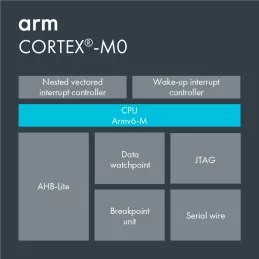
Small, Low Power, Energy Efficient 32-bit Microcontroller Processor
- Exceptional code density - on average, the mix between 16-bit and 32-bit instructions yields a better code density when compared to 8-bit and 16-bit architectures. This has significant advantages in terms of reduced memory requirements and maximizing the usage of precious on-chip Flash memory.
- Binary upward compatible with all other Cortex-M processors - the Cortex-M0 has mainly 16-bit Thumb-2 instructions and few 32-bit ones. These instructions are also present on all the other Cortex-M processors. Hence all code written for the Cortex-M0 will run as is on the other processors.
- Built-in low-power features - sleep, deep sleep and state retention are three low power modes available to the user
- Optional Debug Access Port and Serial Wire Debug - for devices where every pin counts the serial wire debug port uses only two pins
-
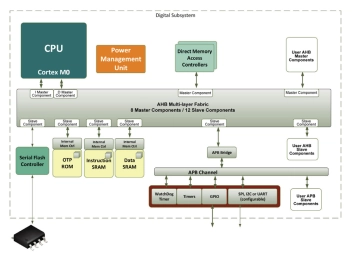
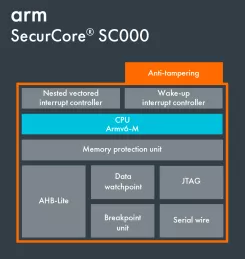
AHB Performance Subsystem - ARM Cortex M0
- The AHB Performance Subsystem is an AMBA® based system that is useful as the digital infrastructure for building low power SOCs needing additional performance.
- This AHB Multi-matrix system contains a flexible Power Management Unit for controlling power sequencing of the CPU and peripherals.
- The PMU can easily be extended to control additional cores, peripherals and even analog subsystems on the same SOC
-
-
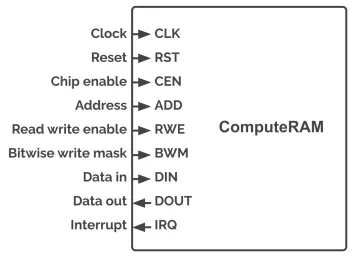
ComputeRAM
- Available as a 18 kB macro in GlobalFoundries 22FDX process; - Memory Compiler and FinFET variants under development
- Low power sleep mode with data retention
- Built using proven foundry SRAM bit cells, fully CMOS, strictly obeys foundry DFM/DRC rules
- Bit-accurate computation
-
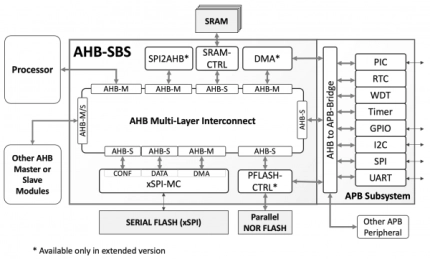
AHB Subsystem
- The AHB-SBS is an integrated, verified, AMBA® 3.0 interconnect and peripherals subsystem ready for embedded applications using processors with AHB bus interfaces such as the BA22-DE, BA22-CE, ARM Cortex-M0/M0+/M1/M3/M4, and several RISC-V processors.
- The AHB subsystem is available in two versions
-
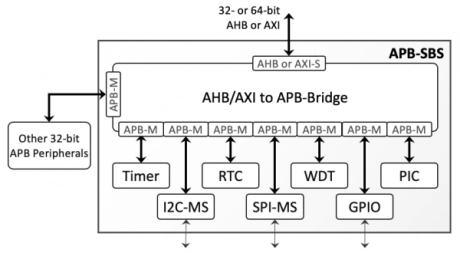
APB Subsystem
- The APB-SBS subsystem integrates typical microcontroller peripherals connected on the an AMBA® APB bus with a bridge to AHB or AXI bus.
- The subsystem is ready for integration with processors having either an AHB or an AXI interface such as the BA2x processors, and several ARM Cortex and RISC-V processors.
- The peripherals connect to the 32-bit APB ports of the APB bridge, which allows configuring the base address and the size of the address space for each peripheral. The subsystem includes the following modules: