32-bit Microcontroller IP
Filter
Compare
51
IP
from
22
vendors
(1
-
10)
-
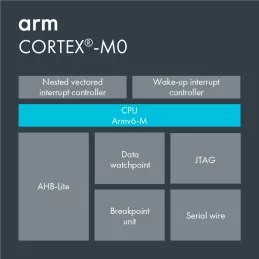
Small, Low Power, Energy Efficient 32-bit Microcontroller Processor
- Exceptional code density - on average, the mix between 16-bit and 32-bit instructions yields a better code density when compared to 8-bit and 16-bit architectures. This has significant advantages in terms of reduced memory requirements and maximizing the usage of precious on-chip Flash memory.
- Binary upward compatible with all other Cortex-M processors - the Cortex-M0 has mainly 16-bit Thumb-2 instructions and few 32-bit ones. These instructions are also present on all the other Cortex-M processors. Hence all code written for the Cortex-M0 will run as is on the other processors.
- Built-in low-power features - sleep, deep sleep and state retention are three low power modes available to the user
- Optional Debug Access Port and Serial Wire Debug - for devices where every pin counts the serial wire debug port uses only two pins
-
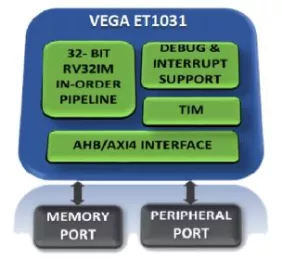
32-bit RISC-V microcontroller
- Leading performance in class with optimized power consumption and area
-
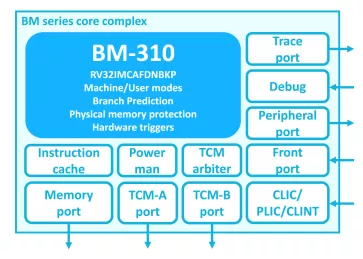
32-bit RISC-V High Performance Microcontroller Class Processor
- RISC-V (RV32IM) ISA
- 3-stage in-order pipeline
- Harvard architecture
- High-performance multiply/divide unit
-
32-bit RISC Processor To Deliver High Performance In Low-Cost Microcontroller Applications
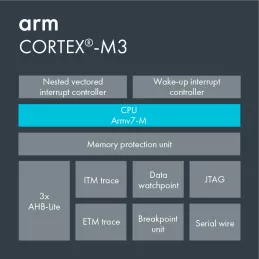
- Powerful debug and non-intrusive real-time trace - Comprehensive debug and trace features dramatically improve developer productivity. It is extremely efficient to develop embedded software with proper debug.
- Memory Protection Unit (MPU) - Software reliability improves when each module is allowed access only to specific areas of memory required for it to operate. This protection prevents unexpected access that may overwrite critical data.
- Integrated nested vectored interrupt controller (NVIC) - There is no need for a standalone external interrupt controller. Interrupt handling is taken care of by the NVIC removing the complexity of managing interrupts manually via the processor.
- Thumb-2 code density - On average, the mix between 16bit and 32bit instructions yields a better code density when compared to 8bit and 16bit architectures. This has significant advantages in terms of reduced memory requirements and maximizing the usage of precious on-chip Flash memory.
-
32-bit RISC-V processor specifically designed for the Automotive and Functional Safety markets
- 32-bit RISC-V ISA
- ASIL B and ASIL D area optimised product variants
- Functional Safety Package and Independent Assessment

-
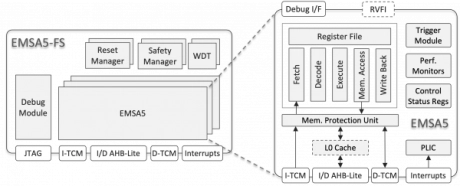
32-bit Embedded RISC-V Functional Safety Processor
- The EMSA5-FS is a processor core designed for functional safety.
- The fault-tolerant processor uses dual or triple instances of the EMSA5, an efficient 32-bit embedded processor IP core implementing the RISC-V Instruction Set Architecture (ISA).
-
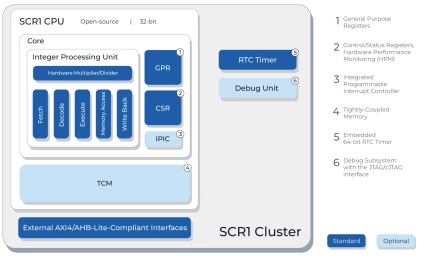
Open-source compact microcontroller core with a 4-stage in-order pipeline for deeply embedded applications
- SCR1 is an open-source and silicon-proven RISC-V-compatible, 32-bit, entry-level, MCU-class core. It targets general-purpose, deeply embedded applications and control systems.
-
MicroBlaze Microcontroller Reference Design
- Simple microcontroller implementation using MicroBlaze, UART, GPIO, and internal block RAM (BRAM) memory
- Includes VHDL design files and project files for EDK/XPS
- Includes "C" code for sample application
- Requires the Xilinx Embedded Development Kit (DO-ML403-EDK-ISE-USB-UNI-G)
-
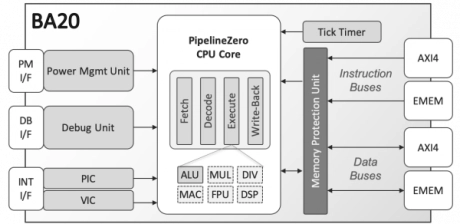
PipelineZero 32-bit Embedded Processor
- The BA20 is a small, ultra-low-power, and very efficient 32-bit processor. It is an excellent step up from the 8051 and other 8- and 16-bit microcontrollers, and ideal for energy-sensitive deeply embedded applications such as wearable electronics, Internet of Things (IoT) sensors, wireless communication, and other mixed-signal ICs.
- Thanks to its PipelineZero™ architecture, the BA20 core delivers a surprisingly high processing efficiency with a tiny silicon footprint.
-
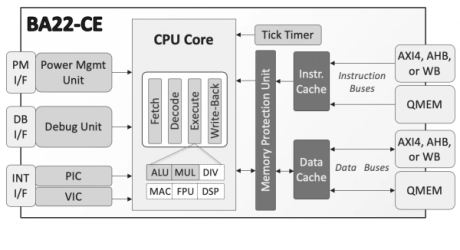
32-bit Cache-Enabled Embedded Processor
- The royalty-free BA22-CE is a 32-bit processor for deeply embedded applications that use off-chip instruction and data memories and that may need to run a real-time operating system (RTOS).
- This processor core is extremely competitive in terms of high performance and low power consumption, and has best-in-class code density.