1T-OTP IP
Filter
Compare
1
IP
from
1
vendors
(1
-
1)
-
FIR Filter Generator
- Direct Form 64-Tap FIR Filter: In the direct form FIR filter, the input samples are shifted into a shift register queue and each shift register is connected to a multiplier. The products from the multipliers are added together to get the FIR filter’s output sample. This example shows a 64-tap FIR filter using 16 sysDSP blocks and approximately 512 slices in the LatticeECP3 FPGA.
- 128-Tap Long Asymmetrical Filters Using Ladder Architecture: Using the ladder architecture, the FIR filter is split into sections each having the same coefficient set as if it was a single continuous filter chain. Instead of connecting the shifted data and the result outputs from the first section to the corresponding input of the next section, the ladder network connects a delayed version of the first stage input data to the second stage input data and sums a delayed version of the first stage sum output with the second stage sum output.
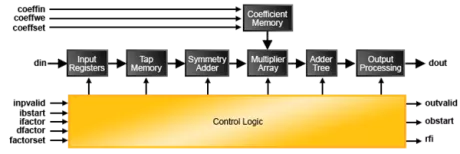
- 256-Tap Long Symmetrical Filters Using Ladder Architecture: The impulse response for most FIR filters is symmetric. This symmetry can generally be exploited to reduce the arithmetic requirements and produce area-efficient filter realizations. It is possible to use only half the multipliers for symmetric coefficients compared to that used for a similar filter with non-symmetric coefficients. An implementation for symmetric coefficients is shown in the figure below. The 256-tap long symmetrical filter example uses only 32 sysDSP slices, 2EBR and 3.5K slices.
- Polyphase Interpolator FIR Filter Designs: The polyphase interpolation filter implements the computationally efficient 1-to-P interpolation filter where P is an integer greater than 1. The example below shows a design with an interpolation by 16 that uses 128 taps. This requires 8 polyphase filters (sub-filters) with 16 coefficients each.