Arm Processor IP
Welcome to the ultimate Arm Processor IP hub! Explore our vast directory of Arm Processor IP
All offers in
Arm Processor IP
Filter
Compare
40
Arm Processor IP
from
2
vendors
(1
-
10)
-
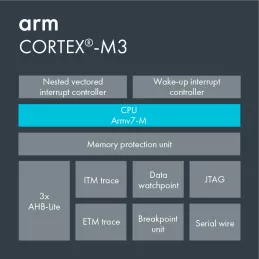
Arm Cortex-A75
Broad market use
Ground-breaking performance
Market-leading efficiency
Brand new memory sub-system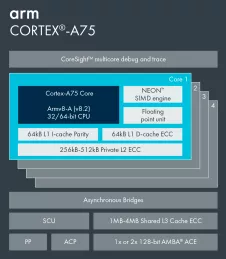
-
Arm Cortex-A55
- Superior efficiency
- New memory subsystem
- State-of-the-art architecture
- DynamIQ big.LITTLE

-
Arm Cortex-A76
- Better experience, user responsiveness, new ML/AI applications and virtual experiences.
- Brings the always-on functionality of mobile to large screen devices, extending battery life for longer experiences.
- 4x performance for inference ML at the edge.

-
Quad core IP platform with integrated Arm security subsystem
- Single channel, video & data processing
-
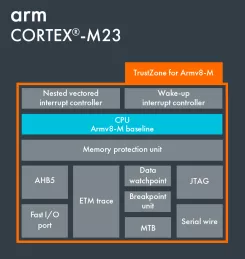
Arm Cortex-M23
- TrustZone for Armv8-M - A foundation for security for embedded devices. TrustZone offers software isolation to code, memory and I/O while retaining the requirements of embedded applications: real-time deterministic response, minimal switching overhead, and ease of software development.
- Energy efficient two-stage pipeline processor - The smallest of Arm processors with TrustZone technology. Brings compactness and energy efficiency while providing support for the full Armv8-M baseline instruction set.
- Memory Protection Unit (MPU) - Software reliability improves when each module is allowed access to specific areas of memory required for it to operate. This protection prevents unexpected access that may overwrite critical data. Each security zone can have a dedicated MPU.
- ntegrated Nested Vectored Interrupt Controller (NVIC) - There is no need for a standalone external interrupt controller. Interrupt handling is taken care of by the NVIC removing the complexity of managing interrupts manually via the processor.
-
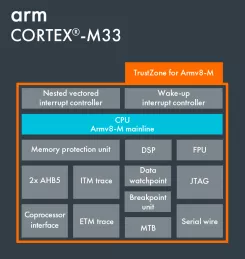
Arm Cortex-M33
- TrustZone for Armv8-M - A foundation for security for embedded devices. TrustZone offers software isolation to code, memory and I/O while retaining the requirements of embedded applications: real-time deterministic response, minimal switching overhead, and ease of software development.
- Co-processor interface - A dedicated bus for extending the operation of the processor with tightly coupled co-processors to handle frequent and compute intensive operations in an ecosystem friendly manner. The interface supports up to eight accelerators and takes into account the security state of the co-processor.
- SIMD, saturating arithmetic, fast MAC - Powerful instruction set for accelerating DSP applications, built right into the processor. A highly optimized DSP library built using these instructions is available free-of-charge from the Arm website (CMSIS Library).
- Memory Protection Unit (MPU) - Software reliability and system security improves when each module is allowed access only to specific areas of memory required for it to operate. This protection prevents unexpected access that may overwrite critical data. Each of the security zones can have a dedicated MPU that may be configured with a different number of regions.
-
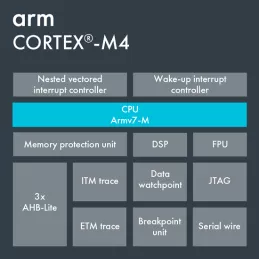
Arm Cortex-M4
- SIMD, saturating arithmetic, fast MAC - Powerful instruction set for accelerating DSP applications, built right into the processor. A highly optimised DSP library built using these instructions is available free-of-charge from the Arm website.
- Powerful debug and non-obtrusive real-time trace - Comprehensive debug and trace features dramatically improve developer productivity. It is extremely efficient to develop embedded software with proper debug.
- Memory Protection Unit (MPU) - Software reliability improves when each module is allowed access only to specific areas of memory required for it to operate. This protection prevents unexpected access that may overwrite critical data.
- Integrated nested vectored interrupt controller (NVIC) - There is no need for a standalone external interrupt controller. Interrupt handling is taken care of by the NVIC removing the complexity of managing interrupts manually via the processor.
-
Arm Cortex-M7
- Optional instruction and data TCMs up to 16MB - Fast access to critical code and data via a dedicated bus. Increases responsiveness to critical events.
- Harvard instruction cache and data cache on 64-bit AMBA 4 AXI interface - Optimises access to large external memories or slow peripherals, reducing latency. Instruction and data caches are optional and separately configurable from 4KB to 64KB.
- SIMD, saturating arithmetic, fast MAC - Powerful instruction set for accelerating DSP applications, built right into the processor. A highly optimised DSP library built using these instructions is available free-of-charge from the Arm website.
- Powerful debug and non-obtrusive real-time trace, with optional full data trace - Comprehensive debug and trace features dramatically improve developer productivity. It is extremely efficient to develop embedded software with proper debug.

-
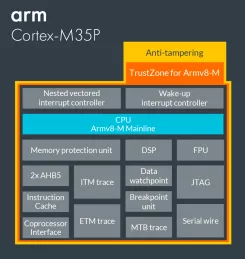
Tamper-resistant Cortex-M processor with optional software isolation using TrustZone for Armv8-M
- Tamper-resistant Cortex-M processor with optional software isolation using TrustZone for Armv8-M
-
32-bit RISC Processor To Deliver High Performance In Low-Cost Microcontroller Applications
- Powerful debug and non-intrusive real-time trace - Comprehensive debug and trace features dramatically improve developer productivity. It is extremely efficient to develop embedded software with proper debug.
- Memory Protection Unit (MPU) - Software reliability improves when each module is allowed access only to specific areas of memory required for it to operate. This protection prevents unexpected access that may overwrite critical data.
- Integrated nested vectored interrupt controller (NVIC) - There is no need for a standalone external interrupt controller. Interrupt handling is taken care of by the NVIC removing the complexity of managing interrupts manually via the processor.
- Thumb-2 code density - On average, the mix between 16bit and 32bit instructions yields a better code density when compared to 8bit and 16bit architectures. This has significant advantages in terms of reduced memory requirements and maximizing the usage of precious on-chip Flash memory.