Nonvolatile Memory IP
Filter
Compare
271
IP
from
37
vendors
(1
-
10)
-
Multiple - Time Programmable Non-Volatile Memory
- Density : 8bits ~ 1024Kbits
- Read voltage : low to 1.0V (LV)
- Write mode : Byte / Word write
- Read mode : Byte / Word read
-
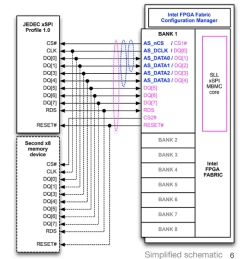
xSPI Multiple Bus Memory Controller
- SLL’s unified xSPI Multiple Bus Memory Controller IP supports the widest range of JEDEC xSPI and xSPI-like NOR Flash and PSRAM memories (JEDEC xSPI Profile 1.0 and 2.0, HyperBus 1.0, 2.0 and 3.0, OctaBus and Xccela Bus) that are available now from many memory vendors.
- JEDEC xSPI and xSPI-like memories offer good performance with lower hardware and power costs. Memory device variants offer up to 512 Mbit PSRAM, up to 2 Gigabit NOR Flash, up to 250 MHz DDR clock speeds, with x4, x8 and x16 data path widths, and a wide range of package options including 4mm x 4mm BGA49 and tiny WLCSP footprints. Some PRSAM devices are now also available with internal ECC.
-
Xccela Flash Memory Model
- Supports Xccela Flash memory devices like MT35X_QLJW_U_256_ABA/ MT35X_QLKA_L_01G_BBA/ MT35X_QLKA_U_02G_CBA from all leading vendors
- Supports 100% of Xccela Flash protocol Standards.
- Supports all the Xccela Flash commands as per the specs.
- Supports Single and double transfer rate (SDR/DDR)
-
Twin Quad NOR Flash Memory Model
- Supports Twin Quad NOR Flash memory devices like MT25T_QLKT_L_01G_xBB from all leading vendors
- Supports 100% of Twin Quad NOR Flash protocol standards.
- Supports all the Twin Quad NOR Flash commands as per the specs.
- Supports Stacked device (two 512Mb die)
-
Serial NOR Flash Memory Model
- Supports Serial NOR Flash memory devices like MT25QL128ABA, MT25QL512ABA, MX25L12835F, MX25L25635F, N25Q032A from all leading vendors like Macronix, Micron, Winbond and many more.
- Supports 100% of Serial NOR Flash protocol.
- Supports all the Serial NOR Flash commands as per the specs.
- Supports Single and Double Transfer Rate (STR/DTR).
-
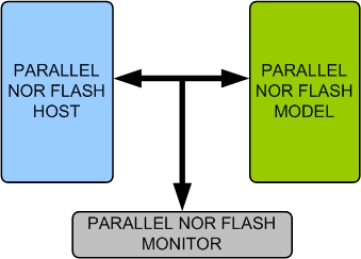
Parallel NOR Flash Memory Model
- Supports Parallel NOR Flash memory devices from all leading vendors.
- Supports 100% of Parallel NOR Flash protocol standard.
- Supports all the Parallel NOR Flash commands as per the specs.
- Supports Asynchronous random/page read
-
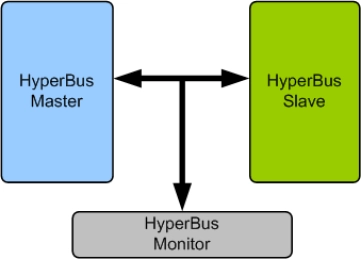
HyperBus Memory Model
- Supports HyperBus memory devices from all leading vendors.
- Supports 100% Cypress HyperBus specification standard.
- Supports all the HyperBus commands as per the specs.
- Supports 512 Mb HyperFlash and 64 Mb HyperRAM.
-
LPDDR5X Secondary/Slave (memory side!) PHY
- JEDEC standard LPDDR5X @ 8533Mbps (Mbits per second per pin)
- Flexible channel architecture – 16- or 32-bit data path widths, supporting either single x32 channel or two x16 channels – 64-bit support, supporting two x32 channels
- Support for byte-mode DRAM devices for high capacity systems
- ZQ Calibration
-
LPDDR5 Secondary/Slave (memory side!) PHY
- JEDEC standard LPDDR5 @ 6400 Mb per second per pin.
- Flexible channel architecture – 16- or 32-bit data path widths, supporting either single x32 channel or two x16 channels – 64-bit support, supporting two x32 channels
- Support for byte-mode DRAM devices for high capacity systems
- ZQ Calibration
-
LPDDR4x Secondary/Slave (memory side!) PHY
- JEDEC standard LPDDR4X @ 4267 Mb per second per pin.
- Flexible channel architecture