Coordinates Conversion IP
Welcome to the ultimate Coordinates Conversion IP hub! Explore our vast directory of Coordinates Conversion IP
All offers in
Coordinates Conversion IP
Filter
Compare
7
Coordinates Conversion IP
from
3
vendors
(1
-
7)
-
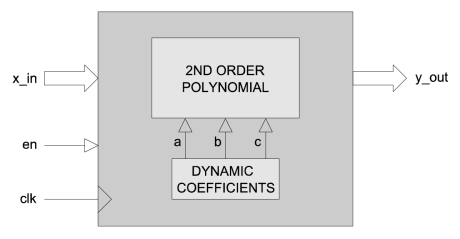
Sine Function
- SIN_X calculates the sine of an angle. It has a fully pipelined architecture and uses fixed-point mathematics throughout.
- Input values are accepted as 16-bit unsigned values in the range 0 to π/2.
- Output values are 16-bit unsigned values in the range 0 to 1.
-
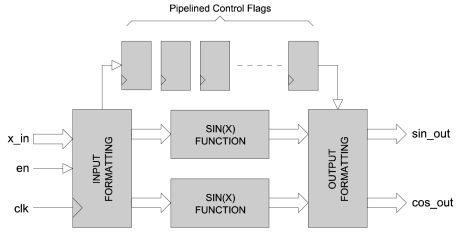
18-bit Sine/Cosine Function
- SINCOS_X calculates the sine and cosine of an angle in radians.
- It has a fully pipelined architecture and uses fixed-point mathematics throughout.
- Input values are accepted as 18-bit signed values in the range -π to π.
- Output values are 17-bit signed values in the range -1 to 1.
-
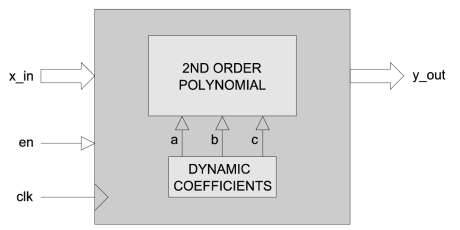
16-bit Cosine Function
- COS_X calculates the cosine of an angle in radians.
- It has a fully pipelined architecture and uses fixed-point mathematics throughout.
- Input values are accepted as 16-bit unsigned values in the range 0 to π/2.
- Output values are 16-bit unsigned values in the range 0 to 1.
-
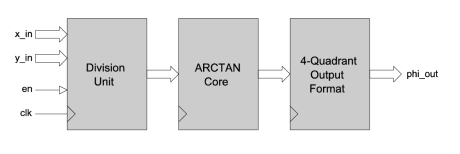
4-Quadrant Arctan Function
- ATAN2_XY calculates the 4-quadrant inverse tangent in the range -π to π. It has a fully pipelined architecture and uses fixed-point mathematics throughout.
- Input values are accepted as 12-bit signed numbers in the range -2048 to 2047.
- The calculated output phase (in radians) is a 19-bit signed value with 1 sign bit, 2 integer bits and 16 fractional bits.
-
Arctan Function
- ATAN_X calculates the inverse tangent of a fraction. It has a fully pipelined architecture and uses fixed-point mathematics throughout.
- Input values are accepted as 16-bit unsigned fractions in the range 0 to 1. Output values are 16-bit unsigned fractions in the range 0 to π/4.
- Both input and output values are in [16 16] format with 0 integer bits and 16 fraction bits.
-
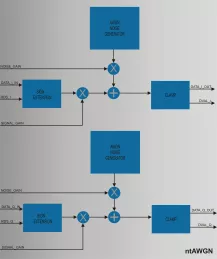
Additive White Gaussian Noise Generator
- High precision AWGN Channel emulator.
- Programmable Pseudo Random Generator(LFSR).
- Programmable number of output bits.
-
CORDIC Algorithm Accelerator
- 24-bit CORDIC rotation engine
- Circular and Hyperbolic modes
- Rotation and Vectoring modes
- Functions: sine, cosine, sinh, cosh, atan, atan2, atanh, modulus, square root, natural logarithm, exp