FFT IP
Welcome to the ultimate FFT IP hub! Explore our vast directory of FFT IP
All offers in
FFT IP
Filter
Compare
268
FFT IP
from 18 vendors
(1
-
10)
-
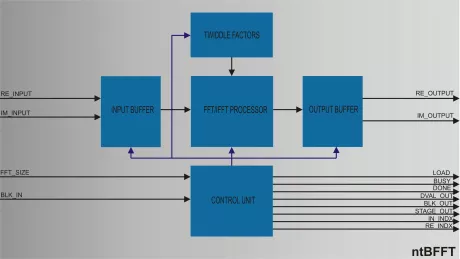
Fully Configurable Radix 2 FFT/IFFT Processor
- Radix-2 Fast Fourier Transform processor IP Core.
- Same IP core may be used to compute both FFT and IFFT transforms without any complexity overhead.
- Highly parameterizable/scalable design using generic I/O fixed point precision and generic internal calculations precision.
- Bit true Matlab script model is provided to aid core fixed point precision configuration for any target application.
-
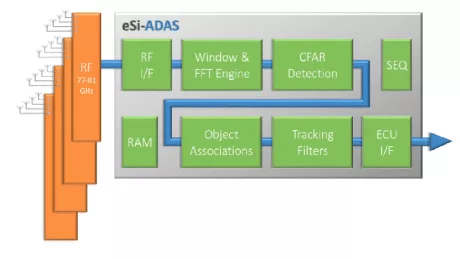
MIMO Radar Co-processor Engine
- Low latency, low power and compact
- Gives ECU headroom for track-to-object recognition and make safety decisions
-
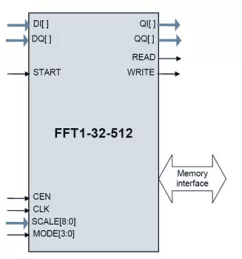
32-512 Point Streaming FFT
- Supports 32/64/128/256/512-point complex FFT and IFFT and can switch dynamically
- Inputs and outputs data in the natural order
- Throughput of 1 sample (In-phase I + quadrature Q) per 4 clocks; no-gap processing of the input data
- Parameterized bit width.
-
ASIP-2
- Platform to design Application Specific Instruction Set Processors (ASIPs).
- Ideal for supporting multi-standard systems.
- Supports a wide range of complex DSP functions.
- The ASIP2 performs Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) to convert time domain signals to frequency domain signals for further processing. It supports FFT sizes from 4 to 8K.
-
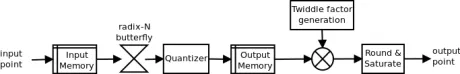
FFT/IFFT Engine
- Supports radix-2/3/4/5
- Parametrized (radix, internal quantization, and FFT size)
- Used as a building block for (I)FFTs and DFTs
- Supports all LTE, WiMAX, DVB and xDSL standards
-
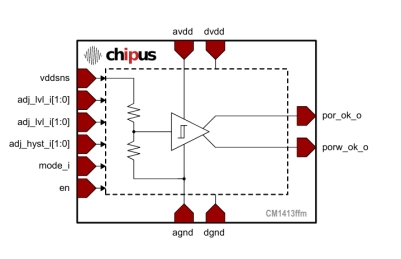
Power-On Reset - Flexible Threshold (1-1.3V), Ultra Low Current (100nA) - SilTerra 0.16µm CL160G
- This macro-cell is an ultra low consumption Power-On Reset (POR) core designed for SilTerra 0.16μm CL160G CMOS technology.
- The threshold sensing voltage can be configured from 1V to 1.3V (default is 1.15V). A hysteresis of 120mV is added to avoid false reset glitches in noisy supplies.
-
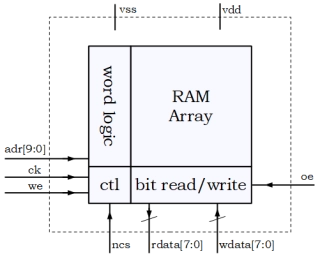
RAM 8b, 16b, and 32b data widths - TSMC 180nm
- 8b, 16b, and 32b data widths available.
- Up to 250MHz clock operation.
- Read and write data busses may tie for single bus operation.
- Available production test RTL.
- VDD 1.6V – 2.0V.
- Data retention to 0.9V.
-
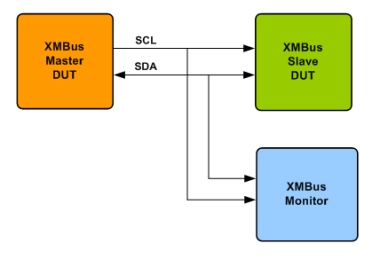
XMBus Verification IP
- Supports XMBus specifications version 0.5.
- Supports XMBus device types: Master, Slave.
- Start, repeated start and stop for all possible transfers.
- Supports 7bit configurable Slave address.
-
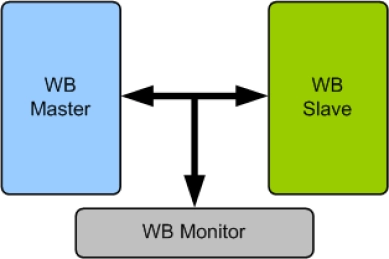
OpenCores Wishbone B3 Verification IP
- Compliant to OpenCores Wishbone B3 Protocol.
- Support for all types of Wishbone devices
- Master
- Slave
-
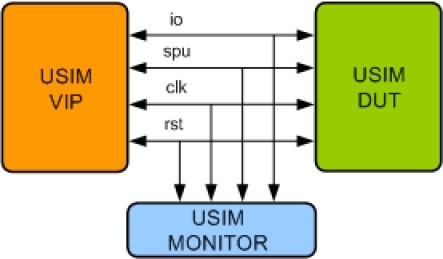
USIM Verification IP
- Compliant with 3GPP TS 31.102 and ETSI TS 102 221 Specification.
- Supports USIM interface between Master and Slave.
- Supports specific command parameters.
- Supports file structures.