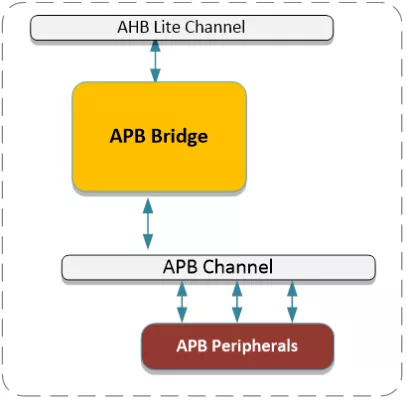
The AHB to APB Bridge translates an AHB bus transaction (read or write) to an APB bus transaction. This is accomplished via two small state machines - one on the HCLK domain and another on the PCLK domain.
The AHB to APB Bridge acts as an AHB Slave, and an APB Master in an AHB/APB subsystem. Typically, the AHB to APB Bridge has its AHB interface connected to a Slave port on an AHB Channel module, and its APB interface connected to the Master port on an APB Channel module.
AHB to APB Bus Bridge
Overview
Key Features
- Translates AMBA® AHB transactions to APB transactions
- Low latency
- Low Gate Count
- Supports APB 2.0 and APB 3.0 Signaling
- Independent HCLK, PCLK pseudo-synchronous clocks
Block Diagram
Deliverables
- Verilog Source
- Complete Test Environment
- AHB Bus Functional Model
- C-Sample Code
Technical Specifications
Maturity
Silicon Proven
Availability
Now
Related IPs
- AMBA AHB to APB Bus Bridge Core
- SPI Controller IP- Master/Slave, Parameterized FIFO, AMBA APB / AHB / AXI Bus
- SPI Controller IP- Master-only, Parameterized FIFO, AMBA APB / AHB / AXI Bus
- I2C Controller IP – Slave, SCL Clock, Parameterized FIFO, APB Bus. For low power requirements in I2C Slave Controller interface to CPU
- AXI to AHB Lite Bus Bridge
- AXI to APB Bus Bridge