The H264-E-CFS IP core is a video encoder supporting the Constrained Baseline Profile of the ISO/IEC 14496-10/ITU-T H.264 standard. It Implements an energy-efficient hardware architecture that is optimized for ultra-low-latency video streaming at low bit rates. No DRAM is required due to the patented Compressed Reference Frame Store (CFS) technology.
The H264-E-CFS encoder requires less than half the silicon area of most hardware encoders—approximately 180K gates—allowing for very cost-effective ASIC or FPGA implementations. Its small silicon footprint, low external memory bandwidth requirements, and zero software overhead enable H.264 coding with an extremely low energy cost. The encoder is able to process beyond Full-HD video when mapped on modern ASIC technologies, and HDTV when mapped on FPGAs.
Despite being small, the H264-E-CFS produces high quality video, especially at low bit rates, and is suitable for systems with low-latency requirements. It uses constant quantization to output video streams of Variable Bit-Rate (VBR), or automatically regulates quantization multiple times within a frame to output Constant Bit-Rate (CBR) streams. In CBR mode it responds rapidly to temporal or spatial changes in the video content. This can be combined with an artifacts-free Intra-Refresh coding implementation to effectively eliminate bit-rate peaks, while preserving the periodic intra-coded references. As a result, the stream buffers can be smaller than those typically required, and the end-to-end latency can be brought down to frame or sub-frame levels. Video quality at low bit rates is preserved, as the encoder intelligently uses block skipping and quantization coefficient thresholding to reduce the bit rate with minimal quality loss, and uses the in-loop deblocking filter to eliminate the blocking artifact.
The core was designed for ease of use and integration. Once initially programmed, it operates without any assistance from the host processor. The core is optionally delivered with a raster-to-block converter, and wrappers for AMBA® AHB, AXI, or AXI-Streaming buses are available.
Customers can further decrease their time to market by using CAST’s integration services to receive complete video encoding subsystems. These integrate the encoder core with video and networking interface controllers, networking stacks, or other CAST or third-party IP cores.
The H264-E-CFS IP core is designed using with industry best practices and is production proven. Its deliverables include a complete verification environment and a bit-accurate software model.
AVC/H.264 Video Encoder with Compressed Frame Store
Overview
Key Features
- Low power AVC/H.264 encoder
- Small silicon footprint
- Optimized for low-latency
- Low-bit-rate video streaming
- Highly (10-15:1) compressed frame store (CFS) with perfect reconstruction (no error/drift) with third party standard decoders; patented technology
- Standard Support
- ISO/IEC 14496-10/ITU-T H.264 Constrained Baseline Profile specification
- Output Annex B NAL byte stream decodable by Baseline and Main Profile decoders
- Input Video Formats
- Progressive 4:2:0 YCbCr input with 8 bits per color sample
- Small and Low Power
- 280k gates & 217k bits of RAM
- Uses less power than competitive hardware H.264 encoders thanks to having under half their silicon footprint and low bandwidth.
- Consumes much less power than any equivalent software, or software-hardware encoder
- Low Latency and Low Bit Rates with Fewer Artifacts
- Constant Bit-Rate (CBR) output for smaller stream buffers and end-to-end latency
- Advanced rate control regulates Qp multiple times within a frame, and rapidly responds to temporal or spatial video variations
- Enables artifacts-free Intra-Refresh to eliminate bit-rate peak of I frames
- Block skipping, Quantized coefficients thresholding, and in-loop deblocking filter improve quality at low bit rates
- Ease of Integration
- Zero CPU overhead, stand-alone operation
- AMBA® Interface Options: DMA-capable AMBA® AHB, AXI or AXI-Streaming
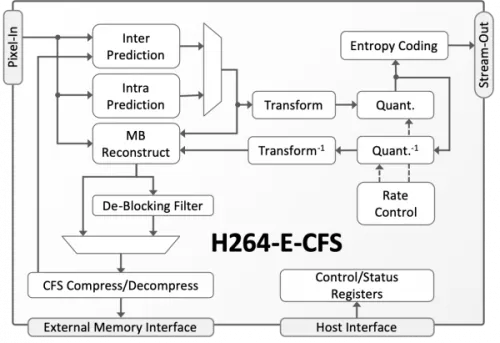
Block Diagram
Deliverables
- Source-code HDL (Verilog or VHDL) (ASICs) or as a targeted netlist (FPGAs)
- Sophisticated self-checking Testbench
- Synthesis scripts
- Simulation script, vectors and expected results
- Software (C++) Bit-Accurate Model and test-vector generator
- Comprehensive user documentation