Filter IP
Welcome to the ultimate Filter IP hub! Explore our vast directory of Filter IP
All offers in
Filter IP
Filter
Compare
33
Filter IP
from
17
vendors
(1
-
10)
-
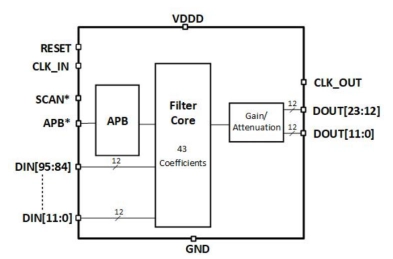
12-bit 250MHz Decimation filter with 43 taps
- Programmable Coefficients
- Programmable gain/attenuation at the output
- 4X Decimation Factor
-
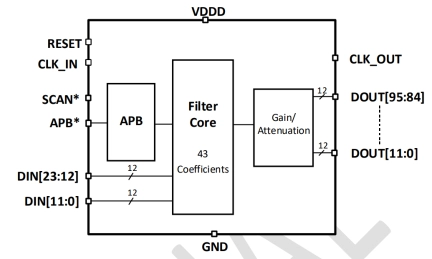
12-bit 250MHz interpolation filter with 43 taps on TSMC 16nm
- The ODT-DSP-INT-43T250M-T16 is a 12-bit 250MHz interpolation filter with 43 taps in a 12/16nm CMOS process.
- The 43 Tap interpolation filter increases output data rate (fDOUT) to the DAC by four relative to its original input data rate(fDIN).
-
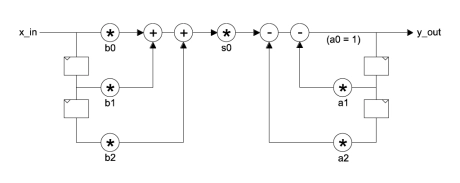
IIR Filter Second-Order-Section
- 2nd order IIR filter sometimes referred to as a 'bi-quad'.
- Internally, it has a fully pipelined architecture permitting the highest possible sample rates for IIR filtering.
- The SOS block is modular allowing any number of SOS blocks to be joined in series to implement higher order IIR filters.
-
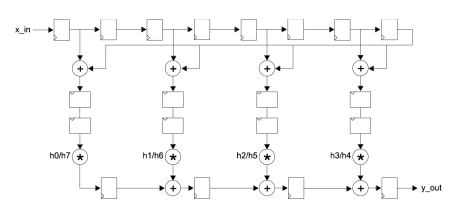
Generic high-speed FIR Filter with symmetry
- FIR filter designed for high sample rate applications with symmetrical coefficients and an even or odd number of taps.
- Features configurable coefficients and data width. Design uses only half the number of multipliers compared to a normal FIR implementation.
- Matlab®, FDAtool and Simulink® compatible.
-
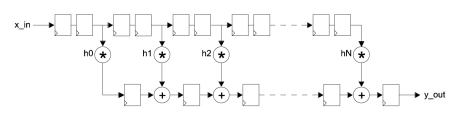
Generic ultra-speed FIR Filter
- FIR filter designed for very high sample rate applications up to 600 MHz.
- Organized as a systolic array, the filter is modular and scalable, permitting the user to specify large order filters without compromising maximum attainable clock-speed. Matlab®, FDAtool and Simulink® compatible.
-
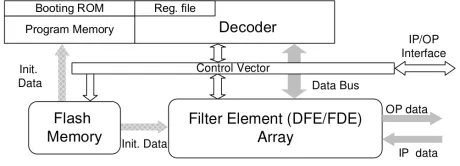
ASIP-1 FFT Engine
- Platform to design Application Specific Instruction Set Processors (ASIPs).
- Ideal for supporting multi-standard systems.
- Supports a wide range of complex DSP functions.
-
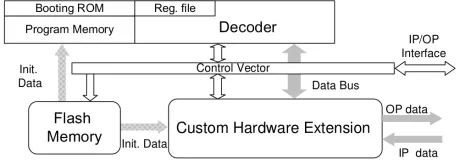
ASIP-2 Programmable Filter Engine
- Platform to design Application Specific Instruction Set Processors (ASIPs).
- Ideal for supporting multi-standard systems.
- Supports a wide range of complex DSP functions
- The ASIP2 performs Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) to convert time domain signals to frequency domain signals for further processing. It supports FFT sizes from 4 to 8K.
-
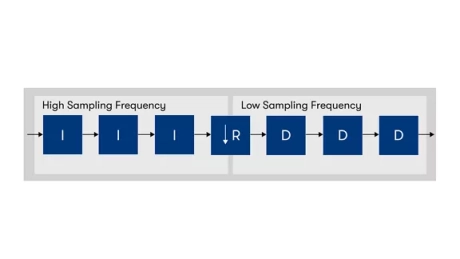
CIC Intel® FPGA IP Core
- The CIC Intel FPGA IP core implements a Cascaded integrator-comb (CIC) filter with data ports that are compatible with the Avalon® streaming (Avalon-ST) interface
- CIC filters (also known as Hogenauer filters) are computationally efficient for extracting baseband signals from narrow-band sources using decimation
- They also construct narrow-band signals from processed baseband signals using interpolation.
-
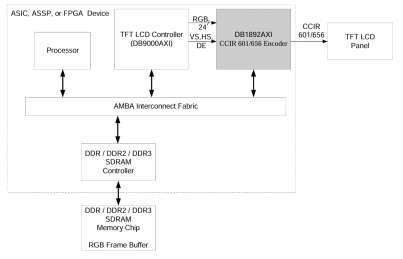
RGB to ITU-R 601/656 Encoder
- The DB1892AXI RGB to CCIR 601 / CCIR 656 Encoder interfaces RGB data along with synchronization signals from a LCD Controller (or any LCD display timing & control unit) to a TFT LCD Panel by-way-of a CCIR 601 / CCIR 656 interface.
-
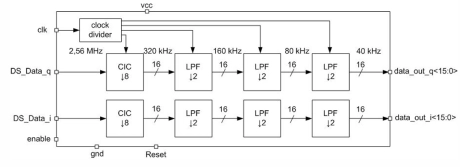
2.56 MHz Digital filter
- SGB25V technology
- Build-in clock former
- Test modes – digital data output
- Operating with complex signal